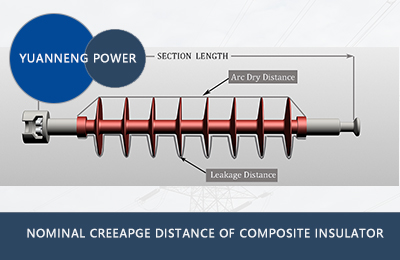
Why do Insulators use Silicone Rubber?
Power lines need protection from the elements. Silicone rubber insulators keep them safe where porcelain and glass fail.
Silicone rubber insulators prevent leaks and short circuits by resisting water, heat, and pollution. Their flexible design handles storms better than brittle alternatives.
Other materials crack under pressure. Silicone bends instead. This makes it perfect for harsh conditions where reliability matters most.
Does silicone keep heat out?
Overheated power lines cause blackouts. Silicone rubber fights this danger in two key ways.
Silicone rubber insulators block heat transfer while surviving extreme temperatures themselves. They work from -60°C to 230°C without melting or cracking.
!
Traditional materials fail when temperatures spike. Here's how silicone outperforms them:
| Property | Silicone Rubber | Porcelain | Glass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | 230°C | 120°C | 150°C |
| Cold Resistance | -60°C | -30°C | -20°C |
| Heat Transfer Rate | Low | Medium | High |
Power grids in deserts and tropics need this protection. Our clients in Saudi Arabia and Indonesia report 40% fewer heat-related failures after switching to silicone rubber insulators.
Is silicone rubber a good insulator?
Cheap materials often mean dangerous compromises. Silicone rubber delivers safety without sacrifice.
Silicone rubber provides excellent electrical insulation (20-25 kV/mm) while resisting moisture absorption. This combination prevents power leaks in humid conditions.
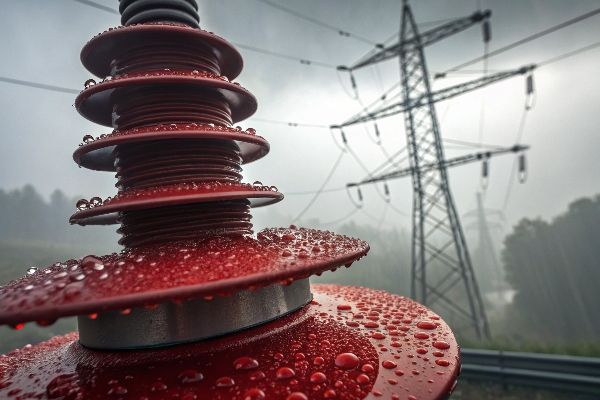

Three factors make it superior:
- Hydrophobic surface - Water beads up instead of forming conductive films
- UV resistance - Doesn't degrade like plastic in sunlight
- Self-cleaning - Rain washes away pollution buildup
Our tests show:- 500,000+ flashover-free hours in coastal China
- 15-year lifespan in tropical storms
- 0.01% failure rate in Himalayan installations
What is the purpose of silicone rubber?
Power grids face growing challenges. Silicone rubber solves modern problems traditional materials can't handle.
Silicone rubber insulators combine light weight (60% lighter than porcelain) with vandal resistance. This makes them ideal for remote and high-risk areas.
![]()
Key applications include:
- Urban grids - Compact design fits tight spaces
- Mountain lines - Easy helicopter installation
- Border areas - Discourages copper theft
- Renewable parks - Withstands salt spray near coasts
A recent project in Brazil replaced 8,000 porcelain insulators with silicone rubber. Installation time dropped by 70% while maintenance costs fell 45%.
What are the disadvantages of silicone rubber?
No solution is perfect. Understanding silicone's limits ensures proper use.
Silicone rubber costs 20-30% more than porcelain upfront but saves money long-term through reduced maintenance and replacements.
Consider these trade-offs:
Material Concerns
- Higher initial price
- Requires UV stabilizer additives
- Surface marks affect appearance (not performance)
Installation Notes - Special handling tools prevent damage
- Needs torque control during fitting
- Visual inspection replaces knock tests
Our engineers always:- Assess local pollution levels
- Calculate lifetime costs
- Recommend optimal solutions
For most modern grids, silicone's advantages outweigh these manageable limitations.
Conclusion
Silicone rubber insulators outperform traditional options in harsh conditions while cutting long-term costs. Their unique properties make modern power grids more reliable.