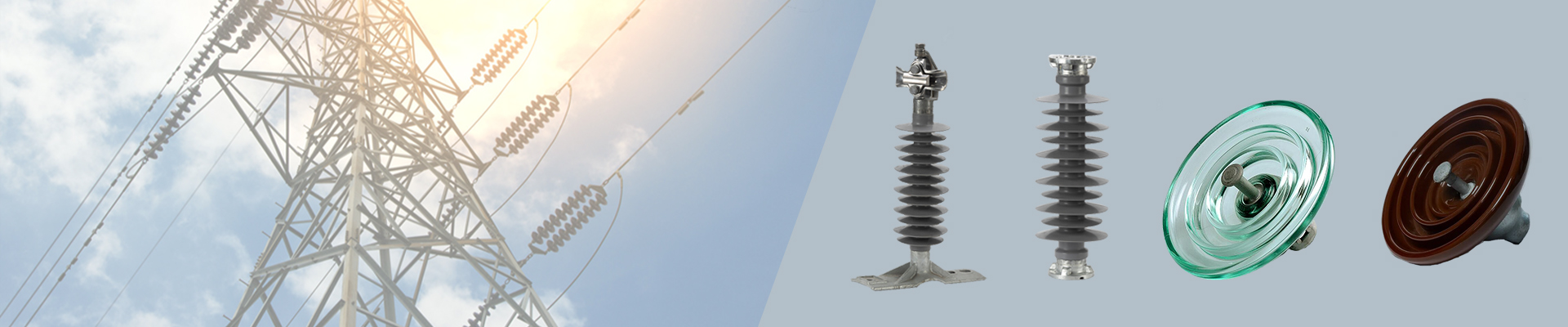
Insulators are components used to support and isolate conductors and towers in power systems, preventing current from flowing between them. According to different materials, insulators are mainly divided into three types: glass, ceramic and composite. Each type of insulator has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, as well as suitable application scenarios.
1. Glass Insulator:
- Advantages: good anti-fouling performance, not easy to form corona or arc on the surface; high mechanical strength and elastic modulus, can withstand certain mechanical loads; light weight and easy to install.
- Disadvantages: Moisture easily condenses on the glass surface, causing air dust to settle on the combined glass surface, providing a path for the system's leakage current; for glass with higher voltage levels, it cannot be cast into irregular shapes because irregular shapes will cause uneven stress distribution and affect its mechanical properties.
- Application scenarios: Mainly used for high-voltage transmission lines in dirty environments, especially those with high requirements for insulation performance.
2. Ceramic Insulators:
- Advantages: good temperature resistance and chemical stability; high strength and excellent electrical properties; good weather resistance, not prone to aging when exposed to outdoor environment for a long time.
- Disadvantages: heavy weight, inconvenient to install; relatively poor impact resistance, easy to break when subjected to excessive force; large amount of energy is consumed during the production process.
- Application scenarios: Widely used in transmission and distribution lines of various voltage levels, especially in low pollution environments.
3. Composite insulators (such as silicone rubber composite insulators):
- Advantages: Excellent anti-pollution flashover performance, suitable for harsh environmental conditions; good elasticity and flexibility, able to adapt to large temperature changes and mechanical loads; low maintenance requirements and long service life.
- Disadvantages: Relatively high cost; may have aging problems compared to other types, especially under strong UV exposure; may have problems with insufficient mechanical strength if not designed properly.
- Application scenarios: Widely used in high voltage and ultra-high voltage transmission lines, especially in coastal areas and severely polluted environments.
Conclusion
When selecting the type of insulator, in addition to considering the characteristics of the material itself, it is also necessary to consider the actual operating environment, including climatic conditions, degree of pollution, mechanical load and other factors, and comprehensively evaluate the economy and reliability.





